01
Reverse Engineering a Wireless Studio Lighting Remote
arduino, arduino hacks, camera, Github, Library, lights, nRF24L01+, Open Logic Sniffer, photo, Photography, radio, radio hacks, remote control, reverse engineer, SPI, strobe Comments Off on Reverse Engineering a Wireless Studio Lighting Remote
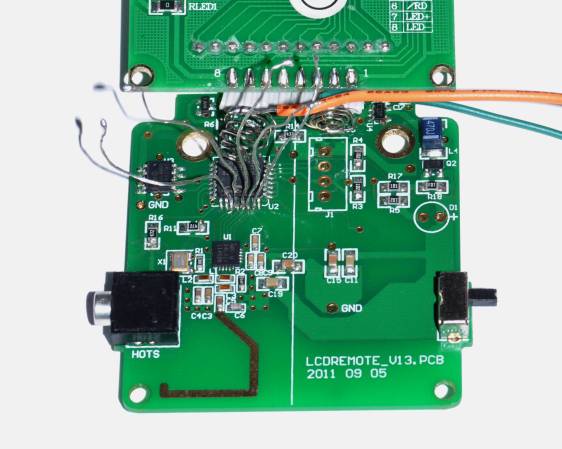
If you want to take a photograph with a professional look, proper lighting is going to be critical. [Richard] has been using a commercial lighting solution in his studio. His Lencarta UltraPro 300 studio strobes provide adequate lighting and also have the ability to have various settings adjusted remotely. A single remote can control different lights setting each to its own parameters. [Richard] likes to automate as much as possible in his studio, so he thought that maybe he would be able to reverse engineer the remote control so he can more easily control his lighting.
[Richard] started by opening up the remote and taking a look at the radio circuitry. He discovered the circuit uses a nRF24L01+ chip. He had previously picked up a couple of these on eBay, so his first thought was to just promiscuously snoop on the communications over the air. Unfortunately the chips can only listen in on up to six addresses at a time, and with a 40-bit address, this approach may have taken a while.
Not one to give up easily, [Richard] chose a new method of attack. First, he knew that the radio chip communicates to a master microcontroller via SPI. Second, he knew that the radio chip had no built-in memory. Therefore, the microcontroller must save the address in its own memory and then send it to the radio chip via the SPI bus. [Richard] figured if he could snoop on the SPI bus, he could find the address of the remote. With that information, he would be able to build another radio circuit to listen in over the air.
Using an Open Logic Sniffer, [Richard] was able to capture some of the SPI communications. Then, using the datasheet as a reference, he was able to isolate the communications that stored information int the radio chip’s address register. This same technique was used to decipher the radio channel. There was a bit more trial and error involved, as [Richard] later discovered that there were a few other important registers. He also discovered that the remote changed the address when actually transmitting data, so he had to update his receiver code to reflect this.
The receiver was built using another nRF24L01+ chip and an Arduino. Once the address and other registers were configured properly, [Richard's] custom radio was able to pick up the radio commands being sent from the lighting remote. All [Richard] had to do at this point was press each button and record the communications data which resulted. The Arduino code for the receiver is available on the project page.
[Richard] took it an extra step and wrote his own library to talk to the flashes. He has made his library available on github for anyone who is interested.
Filed under: Arduino Hacks, radio hacks