31
With the urgency to prevent environmental degradation, reduce waste and increase profitability, farmers around the globe are increasingly opting for more efficient crop management solutions supported by optimization and controlling technologies derived from the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
Intelligent information and communication technologies (IICT) (machine Learning (ML), AI, IoT, cloud-based analytics, actuators, and sensors) are being implemented to achieve higher control of spatial and temporal variabilities with the aid of satellite remote sensing. The use and application of this set of related technologies are known as “Smart Agriculture.”
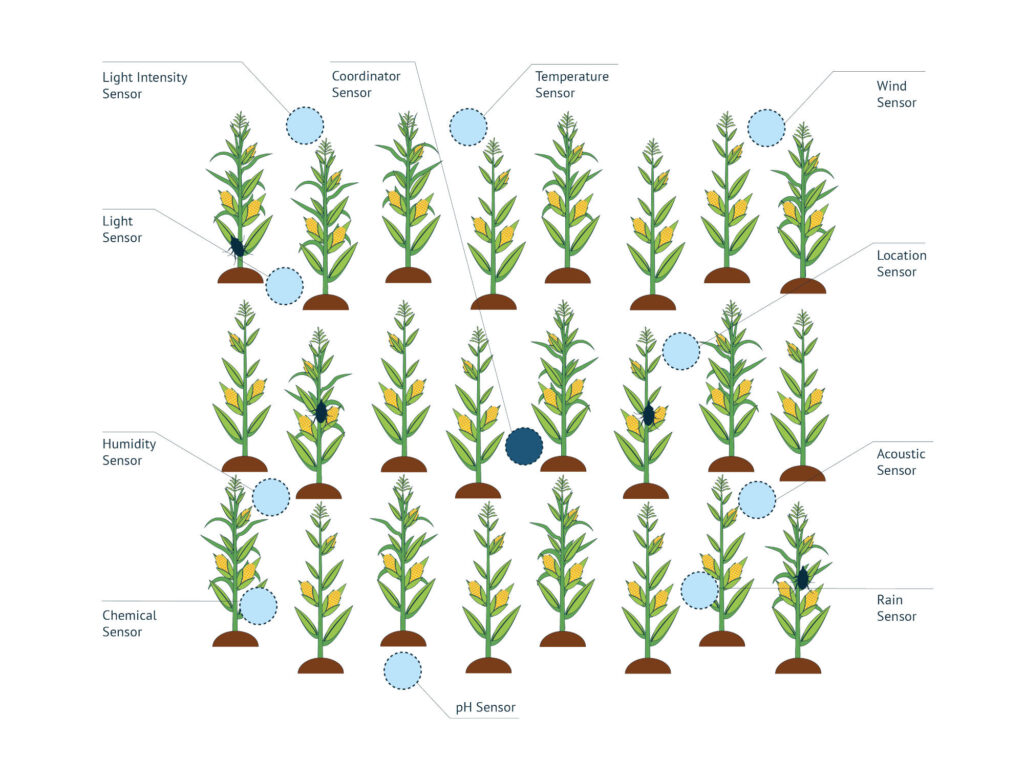
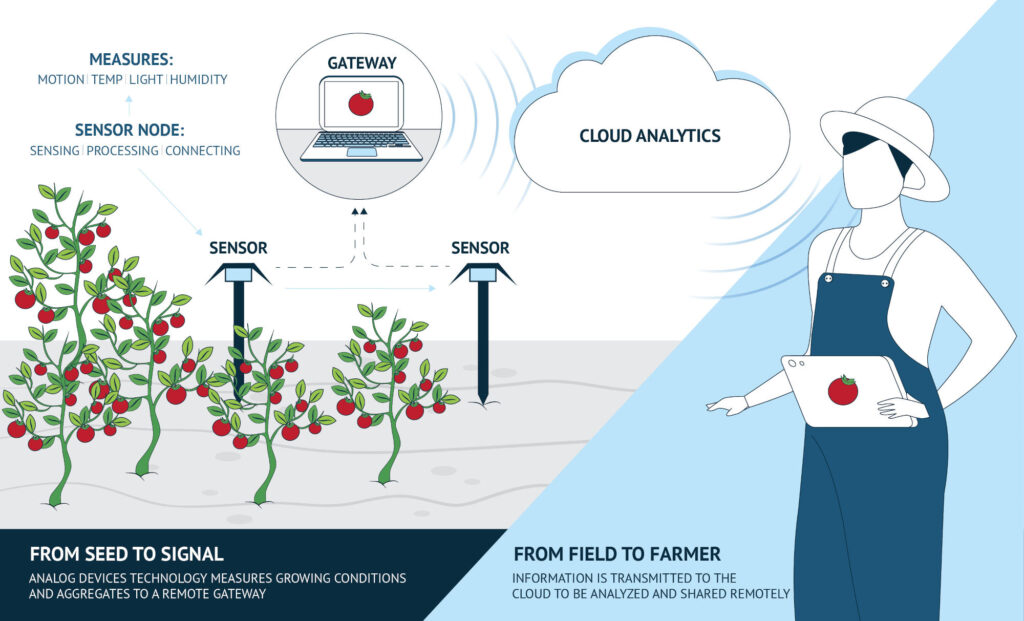
In SA, real-time and continuous monitoring of weather, crop growth, plant physical/chemical variables, and other critical environmental factors allow the optimization of yield production, reduction of labor, and improvement of farming products. Practices such as irrigation management, resource management, production, or fertilization operations are being facilitated by integrating IoT systems capable of providing information about multiple crop factors. In this way, while quality and quantity of production are boosted, the negative aspects of unsustainable and costly agriculture practices are also prevented with advanced interconnected actuators and sensors.
Why Smart Agriculture?
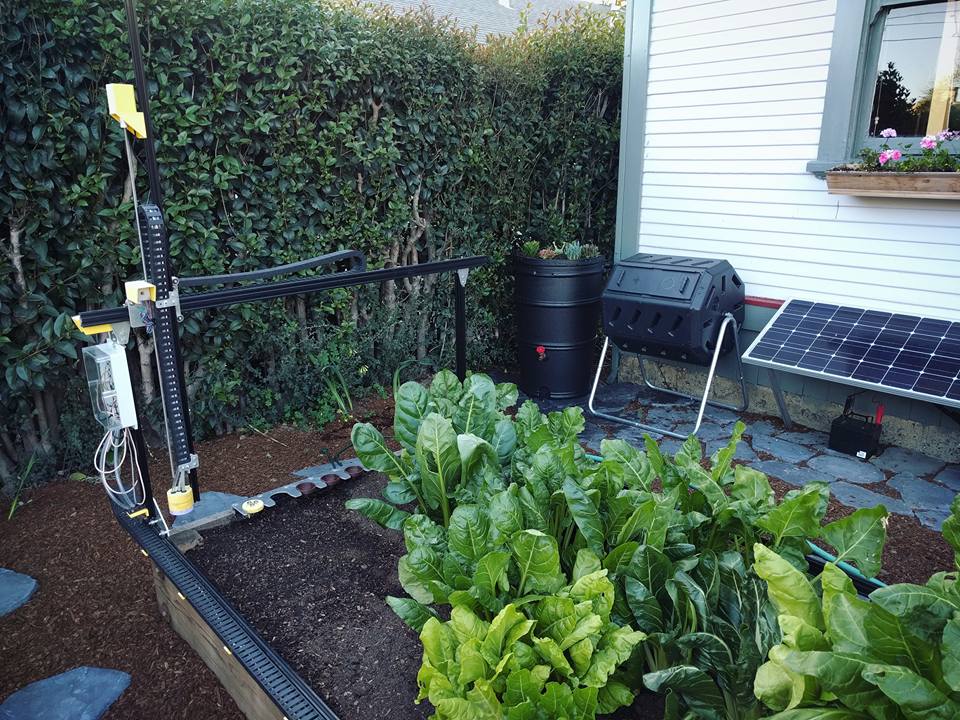
The major focus in this relatively new field is crop optimization through higher productivity and significant control over environmental variations. Smart agriculture provides a convenient way to integrate farming management by having in-hand mobile devices that receive data collected from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV), satellites, or wireless sensors that operate directly at the plant level and are connected, for example, to cloud-based systems.
In general, SA can potentially:
- Reduce water consumption,
- Implement a better plant nursing process with optimized nutrient levels,
- Decrease risk of yield loss,
- Assurance of higher revenue,
- Better yield quality,
- Decrease overall production of waste,
- Simplification of labor,
- Enhance environmental protection.
From small farming to urban gardening
The IoT can provide solutions for small farmers ranging from resource management to climate adaptability. However, urban gardeners or small producers are also benefiting from innovations brought through the evolution of IoT. Figure 4 shows a typical low budget and high precision system designed to improve irrigation in urban gardens.
The system is relatively simple, but it offers the potential easiness of building open-source solutions without significant technical constraints in different setups where adaptation to environmental conditions is required. Basic electromagnetic sensors, power supply, a water pump, relays, and the irrigation system are hardware interconnected and managed via cloud-based monitoring. A control unit receives the data that the user later accesses via the internet.
Technology democratization can boost the competitiveness of small producers.
Despite the tremendous potential of SA, technical issues are just one aspect of the whole story. The deployment of high-tech solutions that are less costly, accessible, reliable, and durable has not yet reached maximum potential. The limited internet coverage in rural areas, especially in emerging economies, slows down the deployment of SA technologies. It is why the democratization of IICT, including the internet, is not a discussion of privilege. It is crucial to support the sustainable transformation of agriculture in which small farmers and rural communities can also benefit from technological development.
To increase the adaptation of IIoT solutions, Arduino Pro has recently launched ARDUINO EDGE CONTROL (AEC). With its ease to adapt to solar-based power supply, AEC offers the power of AI with state-of-the-art connectivity modems. To learn more about how you can use the Edge Control, check out how to get started.
This is an edited version of an article originally published on Wevolver. For references used in this article, check the full piece at Wevolver.
This is an edited version of an article originally published on Wevolver. Please check the original article for references used within this post.
The post Sustainable transformation of agriculture with the Internet of Things appeared first on Arduino Blog.